More On Communication (Especially Non-Verbal Responses)
Introduction
Generally, people think of verbal and non-verbal communications as being distinctly different. However, they are closely entangled.
"...Verbal communication is explicit, and non-verbal implicit. Non-verbal communications include how spoken language is delivered, along with postures, movements, gestures, and even changes in breathing..."
Westland as quoted by Jeremy Sutton, 2022
Generally, non-verbal communication is a more accurate indication of a person's feelings and thinking than verbal communications.
In addition to consider the words spoken, you need to observe how the words are spoken, facial expressions, eye contact, gestures, postures, etc to form a more complete understanding of the message being shared. In fact, there is no substitute for face-to-face communications to get the complete message.
At times non-verbal responses can contradict verbal responses; and non-verbal responses are more likely to be believed.
Non-verbal responses are part of communication, ie
"...1. Conveying a message (spoken language, written words, intonation, gesture, body language, etc)
2. Decoding the message (whether heard, seen, read)
3. Responding or replying based on the interaction (vocal response, or an action)..."
Rogers et al as quoted by Jeremy Sutton, 2022
Communicating is about sharing information.
Ways of communicating
Generally there are 5 ways of communicating
i) verbal (words)
ii) vocal (through your voice and not the words themselves, by using pitch, emphasis, speech rate, volume, articulation, etc)
iii) bodily (including eye contact, gestures, facial expression, posture, etc)
iv) touch (such as soft or firm; which part of the body makes contact like hand, etc)
v) taking action (involving communication and messages, not face-to-face).
Many non-verbal communication skills are deployed unconsciously, ie communicating through posture, gestures, facial expressions, etc. This increases the chance of incorrect messaging and of providing too much or too little information.
As some non-verbal cues are hard to notice, it requires concentration, focus, commitment and practice.
Non-verbal cues
Some non-verbal cues include
- facial expressions (probably the most important non-verbal cue; displays messages of anger, surprise, disappointment, fear, sadness, etc expressed by raised eyebrows, rolling eyes, shape of the mouth and lips, looking away, forehead, nose, tongue, etc)
- gaze (like how much and when we look at somebody conveys the level of interest; helps us gain facial information, etc)
- eye contact (it is more direct than gaze; it can convey anger, interest, attraction, etc; includes the blinking rate, etc)
- gestures (using physical movement to support what you are saying; emotions are conveyed by, for example, a pointed finger, clenched fist, tilting of neck, moving shoulders, use of hands and fingers, etc; gestures add information to our words)
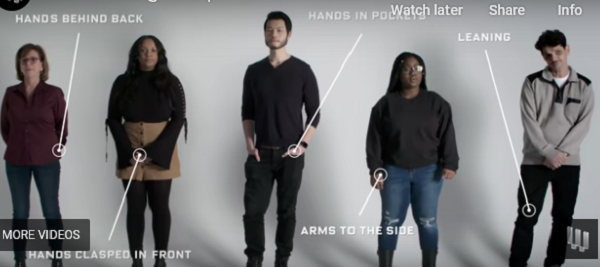
- posture ("...when we physically turn toward someone as they speak or lean forward, we convey interest; facing away or leaning backward can suggest a lack of interest or even boredom. Postures, such as sitting with arms tightly crossed, may express being anxious or uptight..."
Jeremy Sutton, 2022
Linked with posture are movement of head (including handshake), hands, legs, feet, etc
(source: https://positivepsychology.com/nonverbal-communication-cues/)
- breathing (the rate of breathing can indicate various things like nervousneass, anxiety, excitement, etc)
- physical closeness (our culture and personal relationship can impact the degree of comfort with physical closeness; generally there is an intimate zone of 15 to 45 cm reserved for close friends, relatives, partners, etc; with a social zone (1.2 to 3.65 m) for those less well known and a public zone (3.65+ m) for public gathering)
- clothes ("...What you wear can communicate a great deal, including social and occupational standing, ethnicity, conformity, and gender identity. Different age and social groups may respond in various ways depending on the clothes you wear..."
Jeremy Sutton, 2022)
- grooming ("...important information is conveyed by how we care for ourselves, such as being clean and tidy, styling hair, clean-shaven..."
Jeremy Sutton, 2022)
- how you walk (fast walking could indicate keenness, anxiety, etc; while slow walking could indicate disinterest, etc)
Consider style of speech
- talking in one note (a monotone or flat speech that lacks emphasis can indicate insecurity)
- talking on the horizontal (a person may do a lot of talking to fill the space, yet there is little depth to what is said)
- enticing and enthralling (usually skilled at telling engaging stories that helps the listener to make a personal connections)
- runaway train (a cascade of words with no pauses for reflection; sometimes spoken in a high-pitch)
- talking without resolution (while expressive, the person talks without a sense of settlement or outcome)
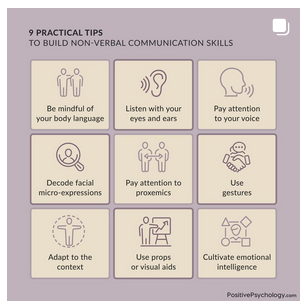
Summary of Non-verbal Responses (including tips)

(source: https://www.instagram.com/positivepsychology_com)
Tips to Build Non-verbal Communication Skills