Some Ways to Look at Organisational Culture (4)
1. Denison Organisational Cultural Model (it involves 4 key components that demonstrates your culture is related to organisational performance:
i) Adaptability (able to adopt to changing patterns, trends, markets, etc; are you listening to the market place and technologies?)
ii) Mission (provides direction, purpose, blueprint, etc; you know where you are going?)
iii) Involvement (involves commitment, ownership, responsibility, etc; are your people aligned and engaged?)
iv) Consistency (involves systems, structures, processes, etc; do your systems create leverage?)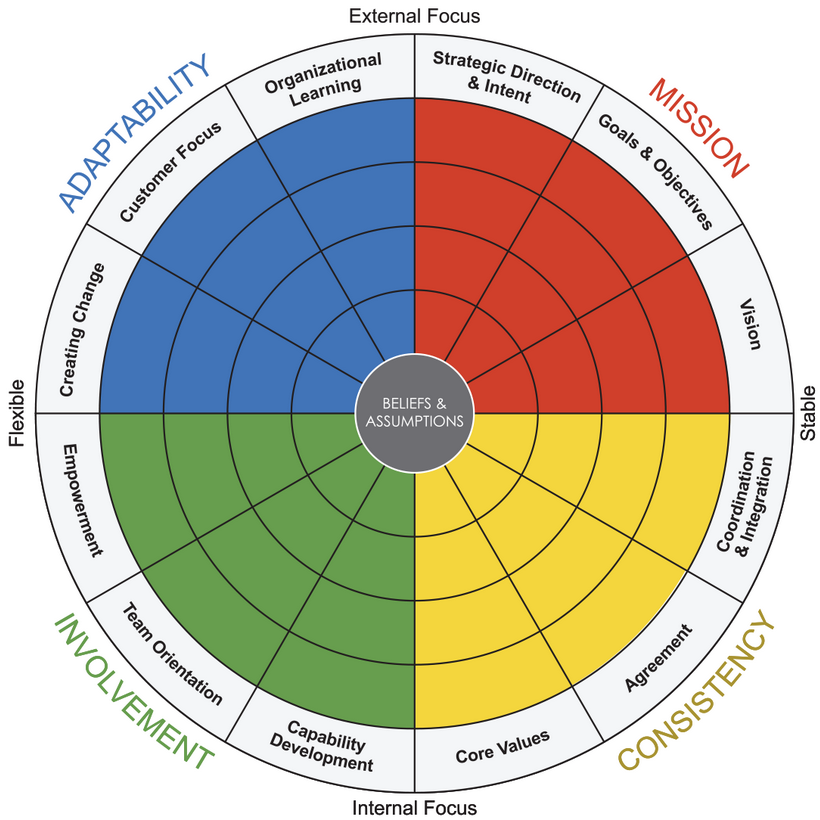
(main source: Domont Consulting, 2023a)
2. Organisational Cultural Inventory (OCI) (this measures behaviour that employees believe is required to 'fit into' the organisation and thus meeting its needs, ie helps identify 12 sets of behaviours (see below diagram) that are currently expected and encourages future ones.
These sets of behaviours are associated with 3 types of organisational cultures:
i) Constructive culture ( organisations that encourage healthy interaction amongst staff)
ii) Passive/defensive culture (staff behave in a way contrary to how they feel and the ideal way)
iii) Aggressive/defensive culture (staff are encouraged to compete against each other and perform better than others)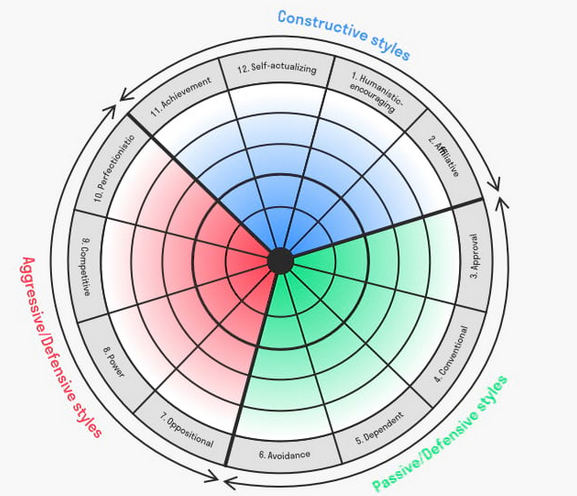
"... Provides a way to see, measure and change the thinking and behavioural styles proven to drive the performance of not only individuals, but also groups and organisations. It enables you to use a common language and visual model for development across 5 levels
- Individual: thinking and behavioural styles of leaders and other key members
- Leader/Manager: impact of leaders/managers on the styles of people around them
- Group: interaction styles of members of problem-solving groups
- Organisation: organisational culture in terms of values ( ideal) and behavioural norm (current)
- Customer: styles exhibited by service providers when interacting with customers..."
Domont Consulting, 2023a)
This framework measures 12 sets of behavioural norms (see above diagram) which are associated with 3 general types of organisational cultures:
(main source: Domont Consulting, 2023a)
3. Hofstede Cultural Dimensions (originally created for national cultures, it can be used for organisational cultures; it allows to examine culture along a range of dimensions like power distance, individualism versus collectivism, uncertainty avoidance, etc (see below diagram); it demonstrates impact of society's culture on the values of its members, and how these values relate to behaviour.
| LOW | Indicators | HIGH |
|---|---|---|
| Egalitarian | power distance | Embraces hierarchy |
| Collectivist | collectivism vs individualism | Individualistic |
| Comfortable with uncertainty | uncertainty avoidance index | Uncomfortable with uncertainty |
| Nurture important | femininity vs masculinity | Power important |
| Traditional and short-term | short-term vs long-term orientation | Futuristic and long-term |
| Normative repression | restraint vs indulgence | Satisfaction is good |
(main source: Domont Consulting, 2023a))
(for more detail, see elsewhere in the Knowledge Base)
4. The Cultural Web Diagram (this involves 6 interrelated components (see below diagram):
i) stories and myths (these reflect the core values and underlying assumptions of an organisation's culture that are based on past events and dominate organisational conversations)
ii) rituals and routines (daily behaviours and actions that demonstrate acceptable behaviour as demonstrated by management; determines people's reactions to different situations)
iii) symbols (they convey meaning about the organisation and include logos, officers, titles, language used, etc)
iv) organisational structure (based on the formal organisational chart; need to understand the informal structure around lines of power and influence that indicates whose contributions are most value)
v) control systems (the ways the organisation is controlled, including financial systems, quality systems, rewarding and recognition systems, etc)
vi) power structures (need to understand the formal and informal lines of power and influence in your organisation;
"...by analysing of these elements, we can paint a picture of the shared assumptions and 'unwritten rules' that shape our behaviours, perceptions, and attitudes within the organisation..."
Domont Consulting, 2023a
Compare the current cultural state to what is desired and can identify areas of alignment and mis-alignment.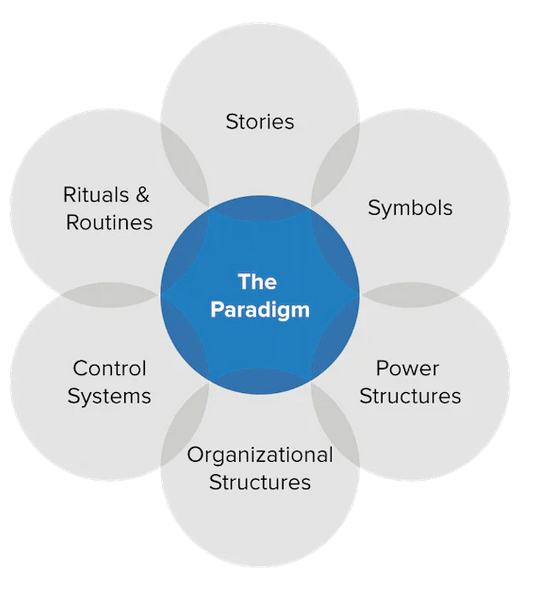
(main source: Domont Consulting, 2023a)
