Organisational Change Portfolio Management (OCPM)
Introduction
OCPM requires understanding the full change landscape (internal and external) of an organisation and the volume of change occurring concurrently in an organisation with multiple projects occurring simultaneously.
If effective it enables organisations to navigate accelerating change with greater agility, effectiveness and efficiency; will help manage and mitigate organisational risk and the negative impact of change, especially on people.
As explained elsewhere in this knowledge base, change management has evolved from
- an art to a discipline
- a primarily technology focus to people and culture
- individual projects to organisational with multiple projects
- from a desirable skill to a core competency, etc.
All this requires an increase in people's capability and capacity to handle organisational change.
Definitions
"...As a group of programs and/or projects managed in a coordinated way support business strategy and to deliver benefits in line with strategic objectives..."
Ernst & Young as quoted by CMI, 2023
"...the continuous assessment of the cumulative change impact on a group of programs, projects and/or initiatives to enable strategic decisions to be made..."
CMI, 2023
Rationale for OCPM
The aim is to improve organisational change maturity and effectiveness; this includes improving overall performance and the likelihood of success of change initiatives while maintaining operational standards.
i) lack of capacity to absorb change, change saturation and change fatigue (with change saturation meaning
"...at that point where an individual or organisation cannot handle additional stress without decreasing overall performance..."
CMI, 2023)
ii) resource conflicts (working out priorities for effective and efficient allocation of resources, including time, for multiple, simultaneous projects and change initiatives)
iii) identify and mitigate risks (list and prioritise all the potential risks and their impacts; explore ways of mitigating the negative impacts)
iv) fragmented programs and capabilities (need to consider
"...ensuring efforts are not duplicated, management of inter-project dependencies, aligning change initiatives with the organisation's strategic goals, and enabling business leaders to manage the change at hand and consider what else is happening, before commissioning another idea..."
CMI, 2023)
OCPM as a process
i) identify portfolios of change and their stakeholders
ii) assess change across program of work
iii) analyse the changes
iv) identify risks
v) prepare and present a change management view of the portfolio and initiatives
(source: Prosci as quoted by CMI, 2023)
OCPM links with organisational change maturity:
i) project change and business readiness context involves
- a focus which is broader than just project delivery
- articulating the need to assess environment in which the change will occur
- understanding other key priorities that may compete with the change
- assessing in detail the impact of the change on different stakeholder groups
NB
"...this level of analysis for individual change initiatives it is critical for change portfolio management to be introduced..."
CMI, 2023
ii) strategic change context (understanding the strategic alignment of the change - irrespective of its scale).
Elements of OCPM
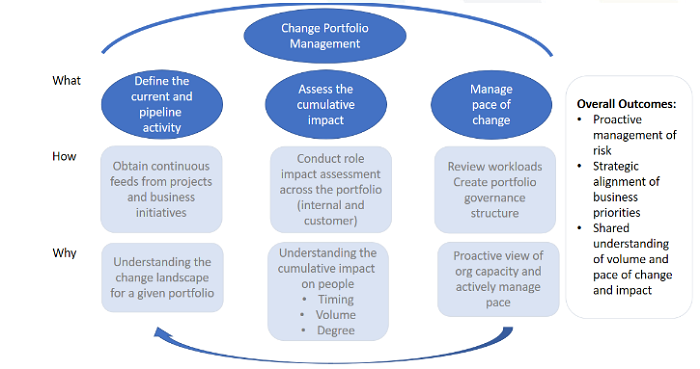
(source: CMI, 2023)
i) define the current and pipeline activities (need to
"...Understand the change landscape and the context of a portfolio, continuous dialogue and feed of information from projects and business activities...... this includes the understanding of the type of change, timing and scale of impact. The feed of project information is supported by......change management methodology and tools and the definitions of key change deliverables and work approach that suits the organisation..."
CMI, 2023)
ii) Assess the cumulative impact (need to consolidate, integrate and assess change across the organisation.
"...this includes centralised information gathering and reporting, to enable the identification of potential risks to business performance, ie time and capacity conflicts..."
CMI, 2023)
iii) managed pace of change (describes the accountability of portfolio management, governance and prioritisation. OCPM
"...decision-making and prioritisation is supported by the consolidated view of change impact and reports on change risk, benefit realisation, and project progress. These insights enable strategic advice to the business via a defined governance process, which is designed to ensure alignment of strategic initiatives with the organisation's operational requirements and strategic goals..."
CMI, 2023)
Challenges to OCPM
i) need to find a balance (between internal and external change resources to best support the organisational change portfolio.)
ii) there is no-one-size fits-all approach (as scope of OCPM can vary, eg program based, functional based, enterprise wide, etc,
"...the scale of portfolio management must be appropriate to the size of the organisation, the number and complexity of change initiatives it faces, and its ability to report on these initiatives..."
CMI, 2023)
iii) which tools are used depends upon the organisation's status
iv) resourcing and size of data (can cause problems for upkeep of information)
Successful outcomes for OCPM
OCPM provides strategic and operational benefits to the organisation and plays a key role in maximising change adoption by
"...1. Proactive management of risk including the capacity of the organisation to absorb the change is at hand
2. Strategic alignment of business priorities. Change story is articulated, and makes sense of how all changes integrate, and how they support the execution of the company strategy
3. Shared understanding of the volume and pace of change. the change portfolio management provides a regular, structured snapshot of the key change effort and creates a standard and common language. This contributes to a meaningful and practical conversation at the management level to enable successful change implementation..."
CMI, 2023
Summary
Despite off-the-shelf solutions, most organisations have to develop their own frameworks and tools that are suitable to their unique situation.
