Empathy gap
Introduction
Most people believe they act in a rational and controlled manner in most situations. However, the empathy gap shows otherwise. It is a cognitive bias that causes people to struggle to understand other people's perspectives that are different to their own. Additionally, they struggle to consider how others' different perspectives can impact their judgement and decision-making.
The main reason people experience empathy gaps is that human cognition is perspective or state-dependent, ie it is strongly affected by your current mental state.
"...the way we process information and make decisions strongly depends on our own mental state at the time..."
Effectiviology, 2021
This makes it difficult to properly evaluate others' mental states or to predict their influence. You are anchored to our own current mental states.
Some examples of being in distinctly different mental states:
- 'cold-to-hot' empathy gap occurs when someone is in a cold (emotional-neutral) perhaps calm, satisfied, etc state, and has trouble understanding someone in a hot (emotional) state such as being angry, happy, scared, upset, hungry, craving, etc;
- 'hot-to-cold' empathy gaps occur when someone is in a hot state, and had trouble understanding someone in a cold state
"...the empathy gap has serious implications when it comes to interpreting and predicting people's behaviour, including your own......underestimating the influence of emotions, impulses, visceral drives..."
Effectiviology, 2021
The empathy gap can be
- intrapersonal (own) or interpersonal (someone else), ie they can occur when you are considering your own or someone else's thoughts, emotions and behaviours
- retrospective (past) or prospective (future), ie they can occur when you consider things that happened in the past or will happen in the future
Some examples
i) when misjudging your own emotions and behaviours
- overestimate your ability to stay composed in an upcoming stressful event, if we are currently calm
- overestimate the likelihood that will be able to stop consuming an addictive substance, such as coffee
- underestimate how your own feelings for somebody are impacted by our past judgement, especially if we no longer have the same feelings for that person
ii) misjudging the emotions and behaviours of others
- don't understand why someone who is nervous about something acts the way that they do, if you don't share their feelings on the topic
- don't understand why somebody has different feelings towards you compared with your feelings towards them
- struggle to understand how a person will act when they are angry about something, if you are currently calm
NB The empathy gap can result in your underestimating the influence of visceral drives, like hunger, desire, fear, pain, etc.
"...the empathy gap can cause people to be unprepared in situations where they are affected by various visceral drives to do things that satisfy their instincts, urges, and cravings in the short term, but that also failed to help them accomplish their long-term goals, or to act in a way that they would ideally prefer..."
Effectiviology, 2021
Outgroup empathy gap
It is
"...cognitive bias that causes people to be more empathetic towards members of their ingroup and less towards people in the outgroup. Essentially, this means that people are more likely to understand and share the mental state of those that they identify as part of their social group..."
Effectiviology, 2021
Different groups can have a common interest like ethnicity, politics, social, sporting, etc
This gap can result in the need to form boundaries around one social group, in order to regulate to whom one extends trust and help.
The empathy gap can be exaggerated by increased anxiety.
"...some factors such as perceived fairness, cultural factors, and a preference social hierarchy, can also influence the likelihood that people display empathy or this type of generalised empathy gap..."
Effectiviology, 2021
There are various techniques to reduce the empathy gap and/or its influence like
- visualising how you would feel in different mental states and perspectives (instead of trying to figure out what you will do, you need to understand how you will feel and what you will be thinking, ie
"...The more you get inside their head and see things from their perspective, the better you can mitigate the influence of the empathy gap..."
Effectiviology, 2021)
- explain the different perspectives (explain the rationale behind the actions and feelings of the different participants)
- contemplating how others would act in similar situations (allows you to analyse the situation in a more detached and emotionally neutral manner)
- consider past actions (don't ignore the past as it is generally a strong indicator of how you are most likely to feel, think, act, etc; your past will give an accurate picture of how you most likely will act in the future; modify your actions so that you behave in a different way)
- use general debiasing techniques (like slowing down your reasoning process; increasing your awareness of the bias; increasing your personal accountability for decision-making)
Linked with the empathy gap is the egocentric bias, ie
"...people rely too heavily on their own point of view when they examined events in their life or when they tried to see things from other people's perspective..."
Effectiviology, 2021
Impact of hybrid working on the empathy gap
- more transactional relationships with organisation
- intra- team connectivity is increasing while organisational connectivity is decreasing
- collaborative networks become more siloed, ie less contact across formal business units
- less informal collaboration
- networks become more static, ie fewer added and/or deleted
- people spend more time alone
- transfer of knowledge reduced
- when in analysis mode (data-reasoning), empathy decreases
(source: Pippa Hague, 2022)
NB all the above work against the people side of change, ie developing shared purpose, etc
In summary
"...empathy gaps can be categorised based on whether they are cold-to-hot or hot-to-cold, whether they're interpersonal or interpersonal, or whether they're retrospective or prospective. All these types of empathy gaps have one thing in common: they involve a struggle to understand mental states that are different to our own present state, as well as a similar struggle to understand how such states affect people's judgement and decision making......Refers to the inability to show empathy towards others, or to understand their perspective, thoughts, or emotions, or behaviours......Empathy gaps can play a role in not only the way we predict their future behaviour, but also in the way we examine past actions, as well as in the way we consider other people's actions..."
Effectiviology, 2021
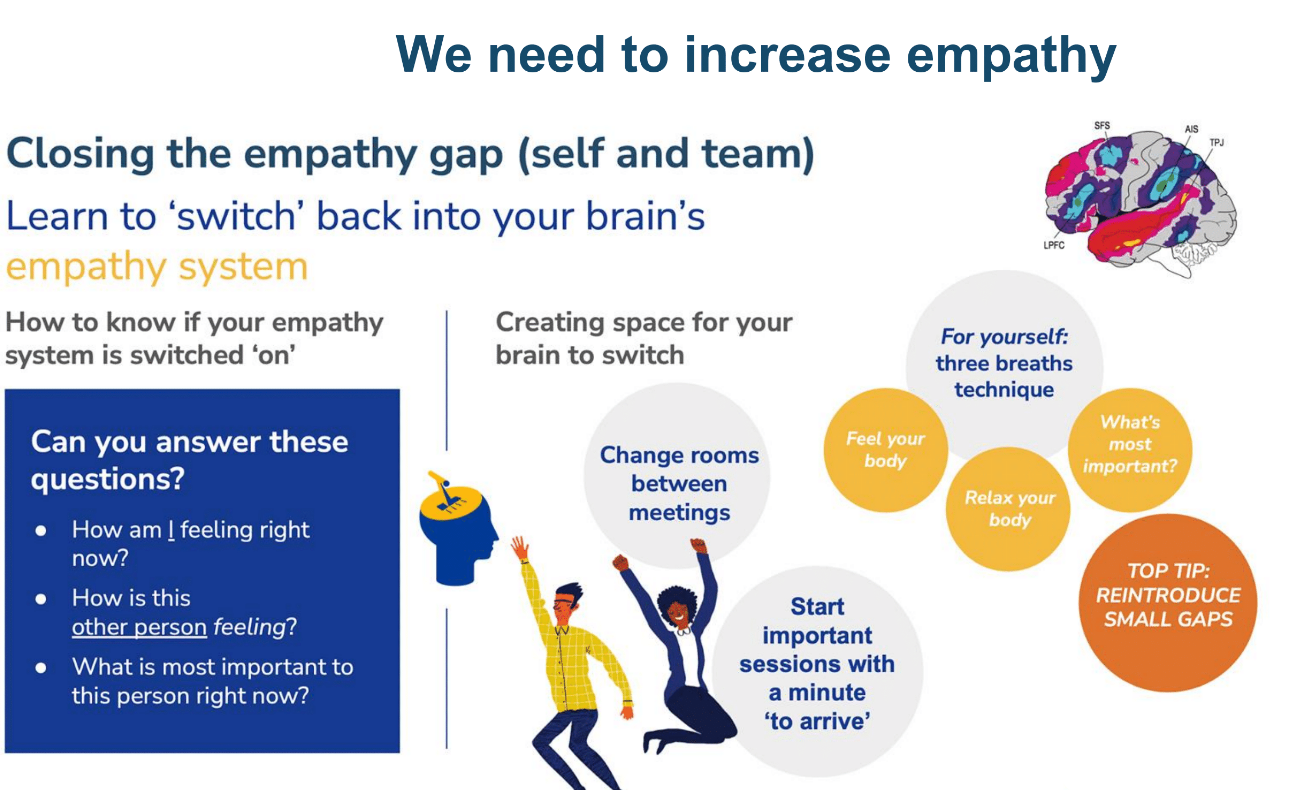
Closing the Empathy Gap
(source: Rethink Change, 2022)
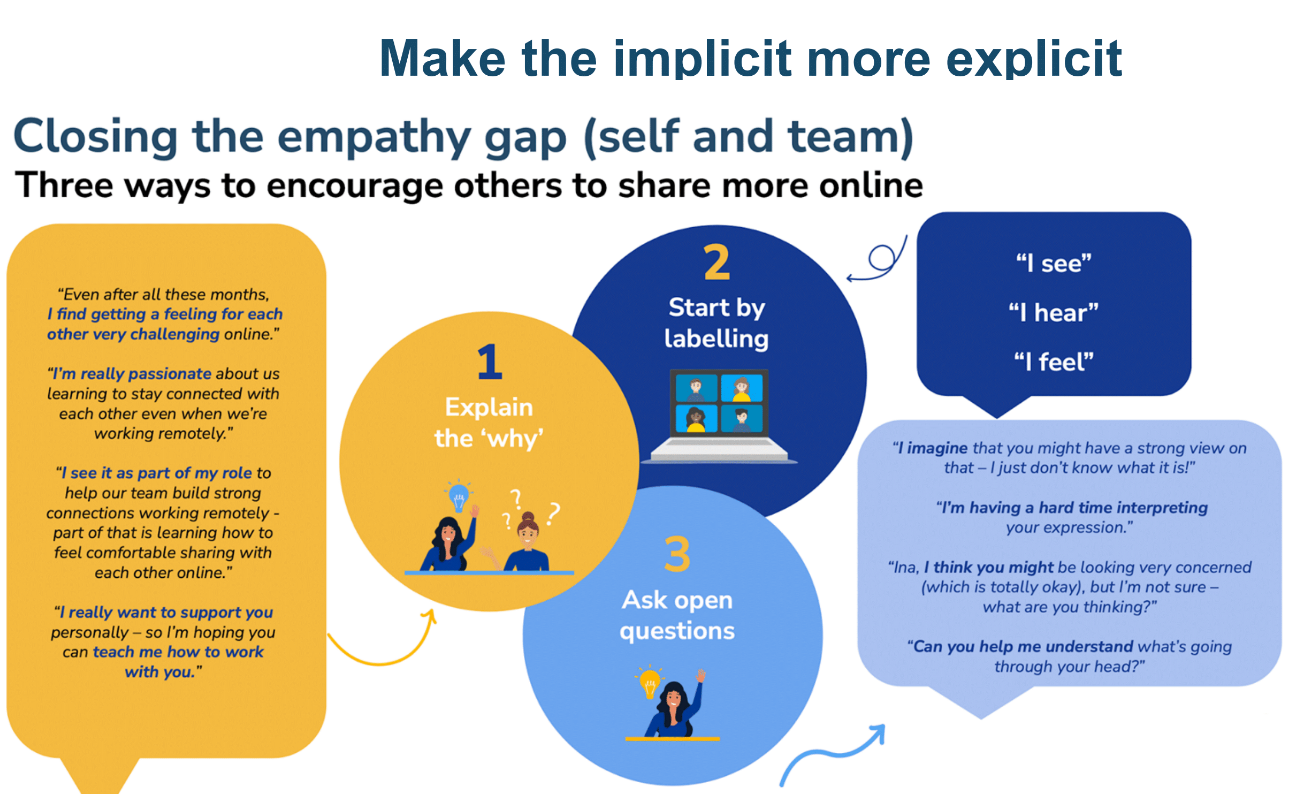
(source: Rethink Change, 2022)
